
- Virtualbox network settings mac address install#
- Virtualbox network settings mac address software#
- Virtualbox network settings mac address license#
- Virtualbox network settings mac address download#
- Virtualbox network settings mac address free#
To create more servers, simply clone the server (or clone the base and setup as per the server), but ensuring they have different names when setting the hostname and IP addresses in /etc/network/interfaces. The image below shows the port forward settings on the router NAT adapter 1 - the red circled Host Port should be different than that of client and server. Then you can connect to each VM (with PuTTY or FileZilla) at the same time, simply by specifying a different port. 5022, 5023, 5024 for client, router, server, respectively. However it is important that the Host Port is different for each VM, e.g. Įach VM should have port forwarding for SSH enabled on the NAT adapter.
Virtualbox network settings mac address software#
ping or installing software with sudo apt install. Test by pinging an external website, e.g.
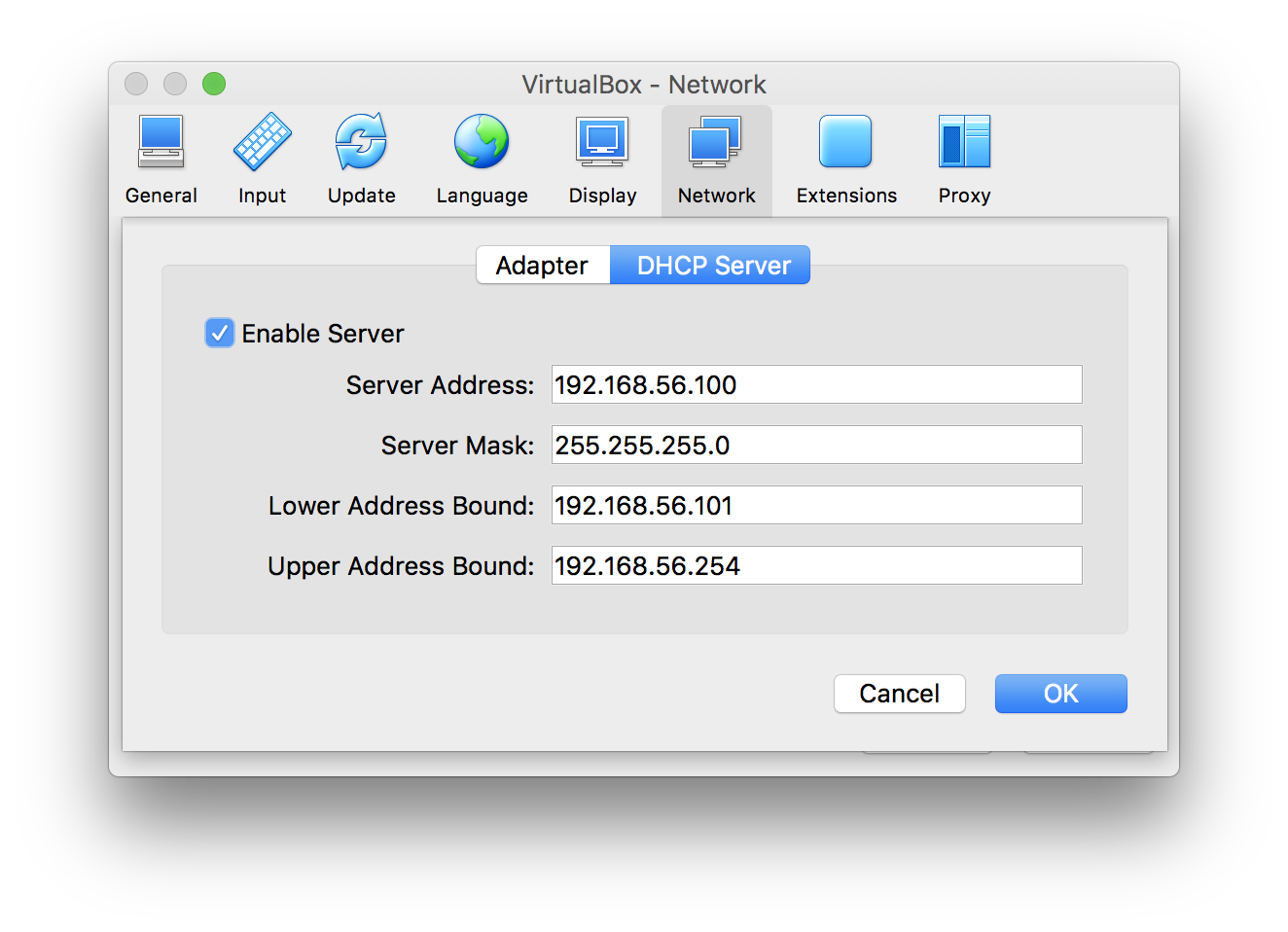
Test the Real InternetĮach VM should still have access to the real Internet. You may also test by SSHing from client to server. If all pings work, then the internal network is working successfully. The output of /etc/hosts and /etc/nf for both client and router is illustrated below. Pre-down route del -net 192.168.0.0 netmask 255.255.0.0 gw 192.168.2.2 dev enp0s8Įdit /etc/nf: sudo vi /etc/nfĪnd uncomment (remove the hash #) the line referring to ip_forward to be: _forward=1 Pre-down route del -net 192.168.0.0 netmask 255.255.0.0 gw 192.168.1.1 dev enp0s8Īdd the following to /etc/network/interfaces: # The internal interface on netb Be sure that the interface names are correct as in the example by running: ifconfig -aĪdd the following to /etc/network/interfaces: # The internal interface on neta In each VM, edit /etc/network/interfaces to setup static IP addresses for the internal interfaces. In the hosts file, change the name for 127.0.1.1 to, where is either client, router or server. Start each VM and set the hostname using: sudo hostnamectl set-hostname Settings for other machines/adapters are similar. The server VM must have two (2) network adapters: NAT and internal network netb.īelow are screenshots of the settings for router adapter 1 (NAT) and router adapter 3 (internal). The router VM must have three (3) network adapters: NAT, internal network neta, and internal network netb. The client VM must have two (2) network adapters, one using NAT and the other using an internal network, e.g.

Be sure to re-initialise the MAC address for each.
Virtualbox network settings mac address install#
Sudo apt install openssh-server man manpages manpages-dev nanoĬreate full clones of the base VM to produce three (3) machines, referred to as client, router and server. Install any software that is necessary on all machines, e.g. Setup a base Linux machine using NAT networking ( NOT using bridged or internal networking). You may use different IP addresses, but be sure to make the corresponding changes in /etc/network/interfaces.Ī 32 minute video demonstrating and explaining the steps below is also available:

The aim is to create a (virtual) Internet of 3 Linux VMs within VirtualBox using internal networking, and also allow those VMs access to the real Internet via NAT. After that, the technical support function is automatically activated for a year you can use it in unclear situations.Building an Internal Network in VirtualBox Introduction
Virtualbox network settings mac address license#
Virtualbox network settings mac address free#
Virtualbox network settings mac address download#


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
